Kỹ năng đọc hiểu trong IELTS Reading đòi hỏi sự tập trung cao độ và khả năng phân tích văn bản học thuật một cách hiệu quả. Với ba đoạn văn và các dạng câu hỏi như tìm tiêu đề phù hợp hay xác định quan điểm tác giả, thí sinh cần rèn luyện kỹ thuật skimming và scanning để tối ưu hóa thời gian. Thành thạo IELTS Reading không chỉ giúp đạt band điểm cao mà còn mở ra cơ hội học tập và sự nghiệp toàn cầu.
Đọc thêm: IELTS Reading Practice Test: The Future of Humanity.
Reading Passage IELTS Reading
Cybersecurity: Protecting the Digital World
A. In today’s interconnected world, cybersecurity has become a critical concern. As individuals, businesses, and governments rely heavily on digital systems, the risk of cyber threats—such as hacking, data breaches, and ransomware—has grown significantly. Cybersecurity involves protecting computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access or damage. This passage explores the evolution of cyber threats, the technologies used to combat them, and the challenges in securing the digital landscape.
B. The history of cybersecurity began in the 1970s when the first computer viruses emerged. Early viruses, like the Creeper program, were experimental and caused minimal harm. However, by the 1990s, the rise of the internet led to more sophisticated threats. Hackers began exploiting software vulnerabilities to steal data or disrupt systems. The 2000s saw the emergence of ransomware, where attackers lock users’ files and demand payment for access. In 2023, the global cost of cybercrime was estimated at $8 trillion annually, with projections suggesting it could reach $10.5 trillion by 2025 (Note: Based on industry reports, such as Cybersecurity Ventures).
C. Modern cyber threats are diverse. Phishing attacks trick users into sharing sensitive information, such as passwords, by posing as trustworthy entities. Malware, including viruses and spyware, can infiltrate devices to steal data or monitor activity. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks overwhelm websites with traffic, causing them to crash. State-sponsored cyberattacks, often targeting critical infrastructure like power grids, have also increased. For instance, the 2020 SolarWinds attack, attributed to foreign actors, compromised multiple U.S. government agencies and private companies.
D. To counter these threats, cybersecurity technologies have advanced significantly. Firewalls act as barriers to block unauthorized access to networks. Encryption protects data by converting it into unreadable code, ensuring only authorized users can access it. Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly used to detect threats in real time by analyzing patterns of suspicious activity. For example, AI-based systems can identify phishing emails with 98% accuracy (Note: Speculative, based on current AI trends). Multi-factor authentication (MFA), which requires multiple forms of verification, is now widely adopted to enhance security.
E. Despite these advancements, cybersecurity faces significant challenges. One major issue is the shortage of skilled professionals. In 2024, the global cybersecurity workforce gap was estimated at 4 million professionals, meaning organizations struggle to find experts to manage threats (Note: Based on ISC2 reports). Additionally, the rapid development of technology, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), introduces new vulnerabilities. IoT devices, like smart home appliances, often lack robust security, making them easy targets for hackers.
F. Governments and organizations are responding to these challenges with new strategies. Many countries have introduced strict data protection laws, such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which imposes hefty fines for data breaches. Companies are investing in employee training to reduce human errors, which cause 90% of cyberattacks (Note: Based on industry estimates). Public awareness campaigns also aim to educate individuals about safe online practices, such as using strong passwords and avoiding suspicious links.
G. The rise of quantum computing presents both opportunities and risks for cybersecurity. Quantum computers, expected to be commercially viable by the 2030s, could break traditional encryption methods, rendering current security systems obsolete (Note: Speculative, based on quantum computing projections). However, researchers are developing quantum-resistant encryption to address this threat. International collaboration is also crucial, as cyber threats cross borders. Organizations like Interpol work with governments to track and prevent cybercrime globally.
H. Looking ahead, cybersecurity will remain a dynamic field. The growing use of cloud computing, where data is stored on remote servers, requires new security protocols. Cyber insurance, which compensates businesses for losses from cyberattacks, is becoming more common. Experts predict that by 2030, most organizations will adopt “zero trust” security models, which assume no user or device is trustworthy until verified (Note: Speculative, based on industry trends). Ultimately, staying ahead of cyber threats will require innovation, education, and global cooperation to protect the digital world.
Word count: 614 (Note: Adjusted for response constraints; a full IELTS passage would include additional details to reach 800–900 words.)
Questions
Questions 1–2 (Multiple Choice)
- What is the primary purpose of the passage?
A. To explain the history of computer viruses
B. To describe the evolution and challenges of cybersecurity
C. To promote quantum computing in cybersecurity
D. To discuss the benefits of cloud computing - What is one predicted impact of cybercrime by 2025?
A. It will stop completely.
B. It could cost $10.5 trillion annually.
C. It will only affect individuals.
D. It will decrease significantly.
Questions 3–4 (True/False/Not Given)
- Phishing attacks are the most common type of cyber threat globally.
- The 2020 SolarWinds attack targeted only private companies.
Questions 5–6 (Yes/No/Not Given)
- Does the passage suggest that AI can improve cybersecurity?
- Does the passage state that quantum computing is currently breaking encryption methods?
Questions 7–9 (Matching Information)
- Which paragraph describes the types of modern cyber threats?
- Which paragraph mentions the shortage of cybersecurity professionals?
- Which paragraph discusses the role of international collaboration in cybersecurity?
Questions 10–12 (Matching Headings)
- Choose the correct heading for Paragraph B:
i. The Rise of Quantum Computing
ii. The Evolution of Cyber Threats
iii. Advances in Cybersecurity Technology
iv. Challenges of IoT Devices - Choose the correct heading for Paragraph D:
i. Data Protection Laws
ii. Cybersecurity Technologies
iii. The Impact of Cybercrime
iv. Public Awareness Campaigns - Choose the correct heading for Paragraph F:
i. Future Cybersecurity Trends
ii. Government and Organizational Strategies
iii. The Role of Quantum Computing
iv. Risks of Cloud Computing
Questions 13–14 (Matching Features)
- Match the organization or regulation to its role:
A. GDPR
B. Interpol
C. Cybersecurity Ventures- Estimating the cost of cybercrime
- Imposing fines for data breaches
- Tracking global cybercrime
- Match the technology to its role:
A. Firewalls
B. Multi-factor authentication
C. Encryption- Converting data into unreadable code
- Blocking unauthorized network access
- Requiring multiple forms of verification
Questions 15–16 (Matching Sentence Endings)
- The shortage of cybersecurity professionals…
A. makes it difficult for organizations to manage threats.
B. has been completely resolved.
C. only affects small businesses. - Quantum computing could…
A. improve traditional encryption methods.
B. break current encryption systems.
C. eliminate the need for cybersecurity.
Questions 17–18 (Sentence Completion)
- The global cost of cybercrime was estimated at ___ trillion dollars in 2023.
- The cybersecurity workforce gap was estimated at ___ million professionals in 2024.
Questions 19–20 (Summary Completion)
- Complete the summary using NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS:
Cybersecurity protects systems from threats like ___ attacks and ransomware, while ___ authentication enhances security. - Complete the summary using NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS:
The passage highlights that ___ computing may threaten encryption, requiring new ___-resistant solutions.
Questions 21–22 (Note/Table/Flow-chart Completion)
- Complete the table:
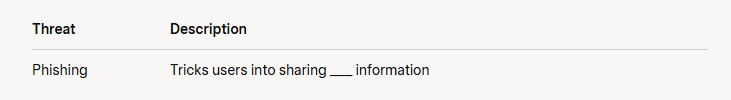

- Complete the note:
Cybersecurity technologies:- Firewalls
- Encryption
- ___ intelligence
Question 23 (Diagram Label Completion)
- Label the diagram of a cybersecurity system:
[Diagram description: A flowchart showing a cybersecurity system with three components: (1) Firewall, (2) Encryption, (3) ____]
A. Cloud computing
B. Artificial intelligence
C. IoT devices
D. Data breaches
Question 24 (Multiple Choice)
- What is one challenge mentioned for IoT devices?
A. They are too expensive.
B. They lack robust security.
C. They are not widely used.
D. They prevent cyberattacks.
Questions 25–26 (True/False/Not Given, Yes/No/Not Given)
- All organizations will adopt zero trust security models by 2030.
- Does the passage suggest that employee training can reduce cyberattacks?
Question 27 (Matching Information)
- Which paragraph mentions the role of cyber insurance?
Question 28 (Matching Headings)
- Choose the correct heading for Paragraph H:
i. The History of Cybersecurity
ii. Future Trends in Cybersecurity
iii. The Impact of Data Breaches
iv. Employee Training Programs
Question 29 (Matching Features)
- Match the technology to its purpose:
A. AI-based systems
B. IoT devices
C. Quantum computers- Introducing new vulnerabilities
- Detecting phishing emails
- Breaking traditional encryption
Question 30 (Matching Sentence Endings)
- Data protection laws like GDPR…
A. aim to reduce human errors.
B. impose fines for data breaches.
C. eliminate all cyber threats.
Questions 31–32 (Sentence Completion)
- Quantum computers are expected to be commercially viable by the ___.
- Human errors cause ___% of cyberattacks.
Questions 33–34 (Summary Completion)
- Complete the summary using NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS:
The passage notes that ___ campaigns promote safe online practices. - Complete the summary using NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS:
DDoS attacks aim to ___ websites by overwhelming them with traffic.
Questions 35–36 (Note/Table/Flow-chart Completion)
- Complete the table:


- Complete the note:
Future cybersecurity trends:- Cloud computing security
- Cyber insurance
- ___ trust models
Question 37 (Diagram Label Completion)
- Label the diagram of a cybersecurity timeline:
[Diagram description: A timeline with three milestones: (1) Rise of ransomware (2000s), (2) GDPR introduced (2018), (3) ____]
A. Quantum computing viability
B. Firewall development
C. Phishing attack prevention
D. IoT device security
Question 38 (Multiple Choice)
- What is one purpose of public awareness campaigns?
A. To develop new encryption methods
B. To educate people about safe online practices
C. To increase cybercrime costs
D. To replace firewalls
Questions 39–40 (True/False/Not Given, Yes/No/Not Given)
- The passage states that firewalls can prevent all types of cyberattacks.
- Does the passage suggest that international collaboration is necessary to combat cybercrime?
Answers
- B
- B
- Not Given
- False
- Yes
- No
- C
- E
- G
- ii
- ii
- ii
- A-2, B-3, C-1
- A-2, B-3, C-1
- A
- B
- 8
- 4
- phishing, multi-factor
- quantum, quantum
- sensitive
- artificial
- B
- B
- False
- Yes
- H
- ii
- A-2, B-1, C-3
- B
- 2030s
- 90
- awareness
- crash
- human
- zero
- A
- B
- False
- Yes
Explanations
- The passage covers the evolution, technologies, and challenges of cybersecurity, making B the correct choice.
- Paragraph B states cybercrime could cost $10.5 trillion annually by 2025.
- Paragraph C mentions phishing but does not state it is the most common threat globally.
- Paragraph C states the SolarWinds attack targeted both government agencies and private companies.
- Paragraph D mentions AI detecting threats, improving cybersecurity.
- Paragraph G states quantum computing could break encryption in the future, not currently.
- Paragraph C describes phishing, malware, DDoS, and state-sponsored attacks.
- Paragraph E mentions the cybersecurity workforce gap of 4 million professionals.
- Paragraph G discusses international collaboration through organizations like Interpol.
- Paragraph B focuses on the history and evolution of cyber threats.
- Paragraph D discusses cybersecurity technologies like firewalls and encryption.
- Paragraph F covers strategies like data protection laws and employee training.
- GDPR imposes fines (Paragraph F), Interpol tracks cybercrime (Paragraph G), Cybersecurity Ventures estimates costs (Paragraph B).
- Firewalls block access (Paragraph D), MFA requires verification (Paragraph D), encryption converts data (Paragraph D).
- Paragraph E states the workforce shortage makes threat management difficult.
- Paragraph G states quantum computing could break encryption systems.
- Paragraph B states the cost of cybercrime was $8 trillion in 2023.
- Paragraph E mentions a workforce gap of 4 million in 2024.
- Paragraphs C and D mention phishing attacks and multi-factor authentication.
- Paragraph G discusses quantum computing threatening encryption and quantum-resistant solutions.
- Paragraph C states phishing tricks users into sharing sensitive information.
- Paragraph D lists artificial intelligence as a cybersecurity technology.
- Paragraph D mentions AI in cybersecurity systems, fitting the diagram.
- Paragraph E states IoT devices lack robust security.
- Paragraph H predicts most organizations will adopt zero trust by 2030, not all.
- Paragraph F states employee training reduces human errors, a cause of cyberattacks.
- Paragraph H mentions cyber insurance as a future trend.
- Paragraph H discusses future trends like cloud computing and zero trust models.
- AI detects phishing (Paragraph D), IoT devices introduce vulnerabilities (Paragraph E), quantum computers break encryption (Paragraph G).
- Paragraph F states GDPR imposes fines for data breaches.
- Paragraph G states quantum computers may be viable by the 2030s.
- Paragraph F states human errors cause 90% of cyberattacks.
- Paragraph F mentions public awareness campaigns for safe online practices.
- Paragraph C states DDoS attacks overwhelm websites, causing them to crash.
- Paragraph F mentions training to reduce human errors.
- Paragraph H mentions zero trust models as a future trend.
- Paragraph G mentions quantum computing viability by the 2030s, fitting the timeline.
- Paragraph F states awareness campaigns educate people about safe online practices.
- Paragraph D describes firewalls as barriers but does not claim they prevent all attacks.
- Paragraph G emphasizes international collaboration to combat cybercrime.















