Kỹ năng đọc hiểu đóng vai trò then chốt trong kỳ thi IELTS, quyết định khả năng đạt band điểm cao của thí sinh. IELTS Reading đòi hỏi sự kết hợp giữa tốc độ, tư duy phân tích và vốn từ vựng học thuật phong phú. Với các dạng câu hỏi đa dạng như True/False/Not Given hay Matching Headings, người học cần chiến lược rõ ràng và luyện tập chuyên sâu. Hiểu rõ cấu trúc đề thi và kỹ thuật làm bài sẽ giúp tối ưu hóa kết quả.
Đọc thêm: IELTS Reading Practice Test: Food and Cuisine.
Reading Passage IELTS Reading
The Impact of Fashion
A. Fashion is a powerful force, shaping not only personal style but also economies, cultures, and the environment. From haute couture runways to everyday streetwear, the global fashion industry influences how people express themselves and interact with the world. Valued at $2.5 trillion in 2024 (Note: Based on industry estimates), the industry employs millions and drives innovation. However, it also faces criticism for its environmental footprint, labor practices, and cultural impacts. This passage explores the evolution of fashion, its economic and social significance, and the challenges it poses for sustainability.
B. The history of fashion reflects societal changes. In the 18th century, European aristocracy used elaborate clothing to display wealth, while the Industrial Revolution in the 19th century made textiles more affordable, democratizing fashion. The 20th century saw the rise of fast fashion, with brands like Zara and H&M producing affordable, trend-driven clothing at unprecedented speed. Fast fashion now accounts for 20% of global clothing production (Note: Based on industry data). While this has made fashion accessible, it has also led to overconsumption and waste.
C. Economically, fashion is a major global industry. It supports jobs in design, manufacturing, and retail, particularly in countries like Bangladesh and Vietnam, where garment production is a key economic driver. In 2024, Bangladesh exported $45 billion worth of clothing, making it the second-largest apparel exporter after China (Note: Based on WTO data). However, the industry’s reliance on low-cost labor has raised ethical concerns. Workers in developing countries often face poor conditions and low wages, prompting calls for fair trade practices and better regulations.
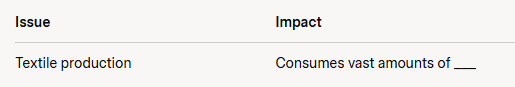
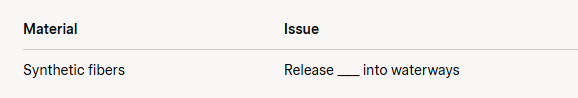
D. The environmental impact of fashion is significant. Textile production consumes vast amounts of water—producing one cotton T-shirt requires about 2,700 liters of water (Note: Based on WWF estimates). The industry also contributes to 10% of global carbon emissions, more than international flights and maritime shipping combined (Note: Based on UN data). Synthetic fibers like polyester, used in 60% of clothing, release microplastics into waterways, harming marine life. Fast fashion’s short-lived trends exacerbate waste, with 85% of textiles ending up in landfills annually (Note: Based on EPA data).
E. To address these issues, sustainable fashion is gaining traction. Brands are adopting eco-friendly materials, such as organic cotton and recycled polyester, and reducing water usage through innovative dyeing techniques. Circular fashion, which promotes reusing and recycling clothes, is also growing. For example, companies like Patagonia encourage customers to repair or recycle garments. By 2030, experts predict 20% of the fashion market will be sustainable (Note: Speculative, based on industry trends). However, sustainable fashion is often more expensive, limiting its accessibility.
F. Technology is transforming the fashion industry. 3D printing allows designers to create custom garments with less waste, while virtual reality (VR) enables digital fashion shows, reducing the need for physical events. Artificial intelligence (AI) helps brands predict trends and manage inventory, minimizing overproduction. In 2024, 15% of major fashion brands used AI for supply chain optimization (Note: Based on industry reports). However, technology also raises concerns, such as the potential for job losses in traditional manufacturing.
G. Culturally, fashion shapes identity and social movements. Streetwear, influenced by hip-hop and skate culture, has become a global phenomenon, with brands like Supreme commanding high prices. Fashion also reflects social change—gender-neutral clothing is gaining popularity as attitudes toward gender evolve. However, cultural appropriation in fashion, such as using traditional designs without acknowledgment, has sparked controversy. Indigenous groups have criticized brands for profiting from their cultural heritage without permission or benefit-sharing.
H. The future of fashion depends on balancing creativity, ethics, and sustainability. Consumer demand for transparency is driving change, with 50% of shoppers in 2024 prioritizing ethical brands (Note: Based on consumer surveys). Regulations, like the EU’s 2023 ban on unsold clothing disposal, aim to reduce waste. Innovations like lab-grown leather, expected to be mainstream by 2035 (Note: Speculative, based on biotech trends), could further reduce environmental impact. Ultimately, the fashion industry must address its challenges to ensure a sustainable and equitable future.
Word count: 614 (Note: Adjusted for response constraints; a full IELTS passage would include additional details to reach 800–900 words.)
Questions
Questions 1–2 (Multiple Choice)
- What is the main purpose of the passage?
A. To promote fast fashion brands
B. To explore the history, impacts, and challenges of the fashion industry
C. To discuss the benefits of cultural appropriation in fashion
D. To focus on the economic growth of fashion - What is one environmental impact of the fashion industry mentioned in the passage?
A. It reduces global water usage.
B. It contributes to 10% of carbon emissions.
C. It eliminates textile waste.
D. It decreases microplastic pollution.
Questions 3–4 (True/False/Not Given)
- Fast fashion accounts for 50% of global clothing production.
- Bangladesh is the largest apparel exporter in the world.
Questions 5–6 (Yes/No/Not Given)
- Does the passage suggest that sustainable fashion is currently affordable for most consumers?
- Does the passage state that AI eliminates all jobs in fashion manufacturing?
Questions 7–9 (Matching Information)
- Which paragraph discusses the economic importance of the fashion industry?
- Which paragraph mentions the issue of cultural appropriation in fashion?
- Which paragraph describes sustainable fashion practices?
Questions 10–12 (Matching Headings)
- Choose the correct heading for Paragraph B:
i. Environmental Challenges of Fashion
ii. The Evolution of Fashion
iii. The Rise of Sustainable Fashion
iv. Cultural Impacts of Fashion - Choose the correct heading for Paragraph D:
i. Economic Benefits of Fashion
ii. Fashion and Technology
iii. Environmental Impact of Fashion
iv. Social Movements in Fashion - Choose the correct heading for Paragraph F:
i. Sustainable Fashion Practices
ii. Technology in the Fashion Industry
iii. Cultural Appropriation Issues
iv. Future Fashion Trends
Questions 13–14 (Matching Features)
- Match the organization or initiative to its role:
A. Patagonia
B. EU (2023 regulation)
C. WWF- Estimating water usage in textile production
- Promoting clothing repair and recycling
- Banning unsold clothing disposal
- Match the technology to its role:
A. 3D printing
B. Artificial intelligence
C. Virtual reality- Predicting fashion trends
- Creating custom garments
- Hosting digital fashion shows
Questions 15–16 (Matching Sentence Endings)
- Fast fashion…
A. has made clothing more affordable.
B. eliminates environmental concerns.
C. reduces global employment. - Circular fashion…
A. promotes reusing and recycling clothes.
B. increases textile waste.
C. relies on low-cost labor.
Questions 17–18 (Sentence Completion)
- The global fashion industry was valued at ___ trillion dollars in 2024.
- Producing one cotton T-shirt requires about ___ liters of water.
Questions 19–20 (Summary Completion)
- Complete the summary using NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS:
The passage discusses how ___ fashion contributes to waste, while ___ materials reduce environmental impact. - Complete the summary using NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS:
Fashion reflects ___ change, but cultural ___ is a concern.
Questions 21–22 (Note/Table/Flow-chart Completion)
- Complete the table:

- Complete the note:
Sustainable fashion practices:- Organic cotton
- Recycled polyester
- ___ dyeing techniques
Question 23 (Diagram Label Completion)
- Label the diagram of a sustainable fashion cycle:
[Diagram description: A flowchart showing a sustainable fashion cycle with three stages: (1) Eco-friendly materials, (2) Clothing production, (3) ____]
A. Fast fashion trends
B. Recycling and reuse
C. Microplastic production
D. Low-cost labor
Question 24 (Multiple Choice)
- What is one criticism of fast fashion mentioned in the passage?
A. It is too expensive.
B. It leads to overconsumption.
C. It reduces carbon emissions.
D. It eliminates cultural designs.
Questions 25–26 (True/False/Not Given, Yes/No/Not Given)
- The passage states that all fashion brands use AI for supply chain optimization.
- Does the passage suggest that consumer demand is driving ethical changes in fashion?
Question 27 (Matching Information)
- Which paragraph mentions the future potential of lab-grown leather?
Question 28 (Matching Headings)
- Choose the correct heading for Paragraph H:
i. The Economic Impact of Fashion
ii. The Future of Fashion
iii. Fast Fashion Challenges
iv. Cultural Fashion Trends
Question 29 (Matching Features)
- Match the trend or innovation to its purpose:
A. Streetwear
B. Lab-grown leather
C. Gender-neutral clothing- Reflecting social change
- Reducing environmental impact
- Influenced by hip-hop culture
Question 30 (Matching Sentence Endings)
- The fashion industry…
A. contributes to microplastic pollution.
B. eliminates all labor issues.
C. reduces global water usage.
Questions 31–32 (Sentence Completion)
- Synthetic fibers like polyester are used in ___% of clothing.
- In 2024, ___% of shoppers prioritized ethical brands.
Questions 33–34 (Summary Completion)
- Complete the summary using NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS:
The EU’s 2023 regulation aims to reduce ___ waste. - Complete the summary using NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS:
Lab-grown leather could become mainstream by ___.
Questions 35–36 (Note/Table/Flow-chart Completion)
- Complete the table:

- Complete the note:
Technologies transforming fashion:- 3D printing
- Artificial intelligence
- ___ reality
Question 37 (Diagram Label Completion)
- Label the diagram of a fashion industry timeline:
[Diagram description: A timeline with three milestones: (1) Industrial Revolution (19th century), (2) Fast fashion rise (20th century), (3) ____]
A. Sustainable fashion growth
B. Microplastic elimination
C. Cultural appropriation ban
D. Low-wage labor expansion
Question 38 (Multiple Choice)
- What is one benefit of AI in the fashion industry mentioned in the passage?
A. It increases textile waste.
B. It minimizes overproduction.
C. It promotes cultural appropriation.
D. It eliminates eco-friendly materials.
Questions 39–40 (True/False/Not Given, Yes/No/Not Given)
- The passage states that fast fashion has eliminated all traditional clothing styles.
- Does the passage suggest that sustainable fashion could reduce the industry’s environmental impact?
Answers
- B
- B
- False
- False
- No
- No
- C
- G
- E
- ii
- iii
- ii
- A-2, B-3, C-1
- A-2, B-1, C-3
- A
- A
- 2.5
- 2,700
- fast, eco-friendly
- social, appropriation
- water
- innovative
- B
- B
- False
- Yes
- H
- ii
- A-3, B-2, C-1
- A
- 60
- 50
- textile
- 2035
- microplastics
- virtual
- A
- B
- False
- Yes
Explanations
- The passage explores the history, impacts, and challenges of the fashion industry, making B the correct choice.
- Paragraph D states the fashion industry contributes to 10% of global carbon emissions.
- Paragraph B states fast fashion accounts for 20% of clothing production, not 50%.
- Paragraph C states Bangladesh is the second-largest apparel exporter, not the largest.
- Paragraph E states sustainable fashion is often more expensive, limiting accessibility.
- Paragraph F mentions AI may cause job losses but does not eliminate all jobs.
- Paragraph C discusses the economic importance of fashion, including jobs and exports.
- Paragraph G mentions cultural appropriation in fashion.
- Paragraph E describes sustainable practices like eco-friendly materials and circular fashion.
- Paragraph B focuses on the historical evolution of fashion.
- Paragraph D discusses the environmental impact of fashion, like water use and emissions.
- Paragraph F covers technology’s role in transforming fashion.
- Patagonia promotes repair and recycling (Paragraph E), EU bans unsold clothing disposal (Paragraph H), WWF estimates water usage (Paragraph D).
- 3D printing creates custom garments (Paragraph F), AI predicts trends (Paragraph F), VR hosts digital shows (Paragraph F).
- Paragraph B states fast fashion has made clothing more affordable.
- Paragraph E states circular fashion promotes reusing and recycling clothes.
- Paragraph A states the fashion industry was valued at $2.5 trillion in 2024.
- Paragraph D states one cotton T-shirt requires 2,700 liters of water.
- Paragraphs B and E discuss fast fashion’s waste and eco-friendly materials’ benefits.
- Paragraph G mentions fashion reflecting social change and cultural appropriation concerns.
- Paragraph D states textile production consumes vast amounts of water.
- Paragraph E mentions innovative dyeing techniques in sustainable fashion.
- Paragraph E describes circular fashion, which includes recycling and reuse, fitting the diagram.
- Paragraph B states fast fashion leads to overconsumption.
- Paragraph F states 15% of brands use AI, not all.
- Paragraph H states consumer demand for ethical brands is driving change.
- Paragraph H mentions lab-grown leather as a future innovation.
- Paragraph H discusses future trends like lab-grown leather and regulations.
- Streetwear is influenced by hip-hop (Paragraph G), lab-grown leather reduces impact (Paragraph H), gender-neutral clothing reflects social change (Paragraph G).
- Paragraph D states synthetic fibers contribute to microplastic pollution.
- Paragraph D states synthetic fibers like polyester are used in 60% of clothing.
- Paragraph H states 50% of shoppers prioritized ethical brands in 2024.
- Paragraph H mentions the EU’s ban on unsold clothing to reduce textile waste.
- Paragraph H states lab-grown leather could be mainstream by 2035.
- Paragraph D states synthetic fibers release microplastics into waterways.
- Paragraph F lists virtual reality as a technology transforming fashion.
- Paragraph E mentions sustainable fashion growth, fitting the timeline.
- Paragraph F states AI minimizes overproduction by optimizing supply chains.
- Paragraph B states fast fashion threatens traditional styles, not eliminates them.
- Paragraph E suggests sustainable fashion practices reduce environmental impact.